In the intricate tapestry of human well-being, two threads—nutrition and mental health—are woven more closely than we frequently enough realize. While the food we consume nourishes our bodies, it also subtly shapes the mind’s landscape, influencing moods, cognition, and emotional resilience. As science delves deeper into this complex relationship, a fascinating picture emerges: what we eat might be just as vital for mental clarity and emotional balance as it is for physical strength. this article explores the nuanced connection between nutrition and mental health, uncovering how mindful eating could be a key ingredient in fostering psychological well-being.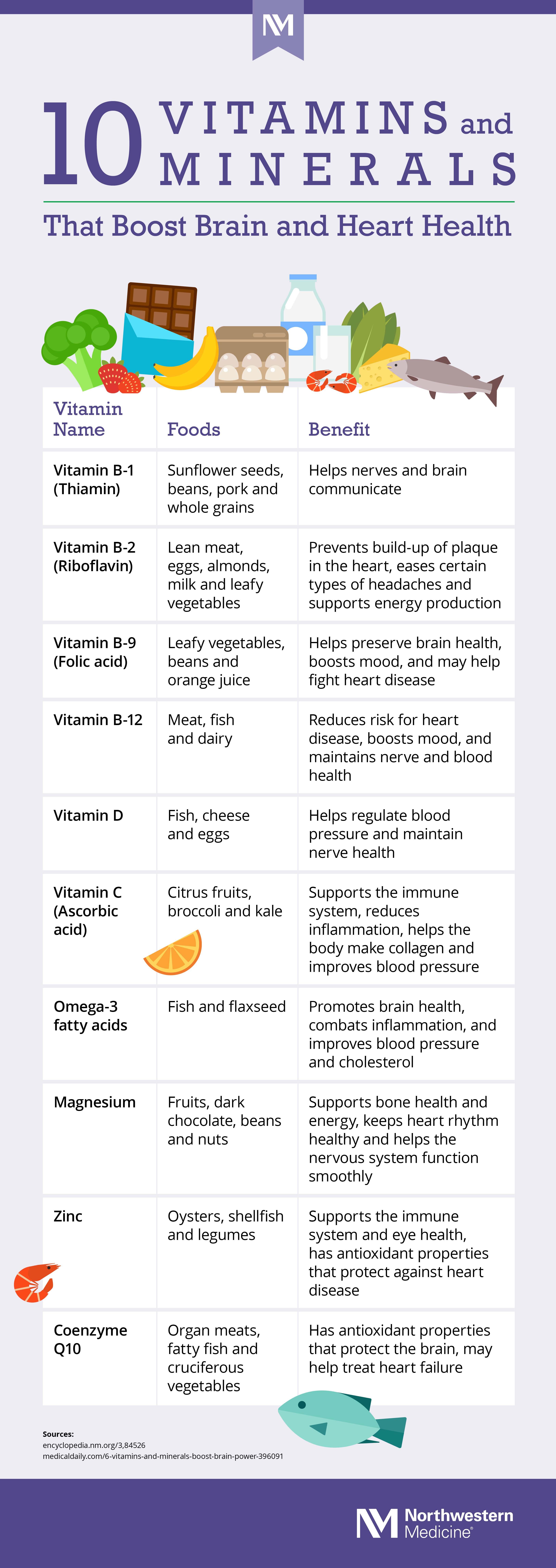
The Role of Key Nutrients in Supporting Brain Function
Certain nutrients play a pivotal role in fueling the brain’s complex processes and maintaining optimal mental health. Omega-3 fatty acids, renowned for their presence in fatty fish, contribute to cell membrane fluidity and neurotransmission, directly impacting cognition and emotional regulation. Additionally, B-vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, act as cofactors in synthesizing neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for mood stabilization. Magnesium, zinc, and antioxidants found in colorful fruits and vegetables further protect neural structures from oxidative stress, promoting brain resilience and clarity.
Incorporating these nutrients into your diet can be simplified by focusing on whole foods rich in brain-supporting elements such as:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) for omega-3s
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale) high in folate
- Nuts and seeds for magnesium and vitamin E
- Whole grains providing steady energy and B-vitamins
- Berries packed with antioxidants
| Nutrient | Brain Benefit | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Supports neuron function and mood | Salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds |
| Vitamin B12 | Enhances neurotransmitter synthesis | Eggs, dairy, fortified cereals |
| Magnesium | Protects against neural inflammation | Almonds, spinach, black beans |
For further detailed insights on nutrition’s role in mental health, reputable sources like the National Institute of Mental Health, NCBI, and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health provide comprehensive research-based information. These resources highlight that the mind is intricately connected to what you consume,emphasizing the transformative potential of targeted nutrition in mental well-being.

Exploring the Gut-Brain Axis and Its Impact on Mood
The intricate dialog between our gut and brain is orchestrated through the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway involving neural, hormonal, and immunological signaling. This connection means that the trillions of microorganisms residing in the gut—collectively known as the gut microbiota—play a pivotal role far beyond digestion. They influence neurotransmitter production, including serotonin, frequently enough dubbed the “feel-good hormone,” which can directly shape mood and emotional well-being. Recent studies suggest that disruptions in this microbial balance may correlate with mood disorders such as anxiety and depression, highlighting the gut as a potential therapeutic target for mental health management. NIMH provides extensive research findings supporting this emerging connection.
Understanding how nutrition modulates this axis opens pathways to enhancing mental health through diet. Nutrients, probiotics, and prebiotics can nurture beneficial bacteria, leading to improved gut barrier integrity and reduced systemic inflammation—key factors that influence brain function. For example, incorporating:
- Fermented foods: yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut
- High-fiber vegetables: asparagus, leeks, garlic
- Omega-3 rich foods: salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts
can foster a flourishing microbiome. The following table outlines some gut-amiable foods and their benefits:
| Food | Primary Benefit | Effect on Mood |
|---|---|---|
| Kefir | Probiotic-rich beverage | Enhances serotonin synthesis |
| Chicory Root | Inulin prebiotic fiber | Improves gut microbial diversity |
| Walnuts | Omega-3 fatty acids | Reduces inflammation-related mood disturbances |
For more scientifically grounded insights on diet, gut health, and their impact on cognition, explore resources at NIH’s National Library of Medicine and World Health Association.Empowering yourself with this knowlege helps in making dietary choices that fuel not just the body, but also nurture mental resilience.

Dietary Patterns That Promote Mental Well-being
Adopting certain dietary patterns can significantly influence mental well-being by regulating mood,reducing stress,and enhancing cognitive function. Diets rich in whole foods—including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins—support optimal brain health through their abundant vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For example,omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon have been associated with lower rates of depression and anxiety,while Mediterranean-style eating emphasizes foods that reduce inflammation and improve neural communication.
Key elements of brain-friendly diets include:
- High fiber intake: Promotes gut health, which is strongly linked to mood regulation.
- balanced macronutrients: Stable blood sugar levels help prevent energy crashes and mood swings.
- Fermented foods: Boost beneficial gut bacteria, influencing neurotransmitter production.
- Low processed sugar and saturated fat: Avoids negative effects on cognition and emotional stability.
| Dietary Pattern | Mental Health Benefits | Key Foods |
|---|---|---|
| mediterranean Diet | Reduces depression risk; improves memory | Olive oil, fish, nuts, vegetables |
| Traditional Japanese Diet | Supports cognitive function; lowers anxiety | Seaweed, tofu, rice, green tea |
| Plant-Based Diet | Boosts mood; decreases inflammation | Legumes, leafy greens, fruits, grains |
Understanding these patterns allows anyone to tailor their nutrition in a way that not only fuels the body but also nurtures the mind. For an in-depth review of dietary impacts on mental health, visit the National Institute of Mental Health, and for practical guidance, explore resources from the Harvard T.H.Chan School of Public Health.

Practical Tips for Integrating Nutritional Strategies into Daily Life
Making nutrient-dense choices can feel overwhelming, but incorporating small, consistent habits can create lasting benefits for mental well-being.Start by preparing simple, balanced meals with a variety of colors on your plate—greens, berries, whole grains, and lean proteins.These foods provide essential antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids that support brain function. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial, as even mild dehydration has been linked to concentration issues and mood fluctuations. Consider setting daily reminders to drink water and opt for herbal teas instead of sugary drinks to maintain steady energy levels.
Another effective approach is to plan meals around your mental health goals.Creating a weekly menu helps ensure you incorporate foods rich in vitamins B, D, and magnesium—known for their mood-regulating properties. Use this simple guide for balance:
| Food Group | Benefits for Mental Health | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Leafy Greens | Rich in folate and antioxidants | Spinach, kale, Swiss chard |
| Fatty Fish | High in omega-3s for brain function | Salmon, mackerel, sardines |
| Nuts & Seeds | Provide magnesium and healthy fats | Walnuts, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds |
| Whole Grains | Stable energy and serotonin production | Quinoa, brown rice, oats |
- Prep meals in advance to avoid turning to processed options during busy days.
- Incorporate mindful eating practices to strengthen the gut-brain connection.
- Regularly update your pantry with fresh, nutrient-rich ingredients.
For additional guidance on nutrition’s impact on cognitive function, visit National Institute of Mental Health or explore research from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. These resources offer evidence-based insights to inspire your journey toward improved mental wellness through diet.
The conclusion
As we unravel the intricate threads linking nutrition and mental health,it becomes clear that what we put on our plates can profoundly shape the landscape of our minds. While food alone isn’t a cure-all, nourishing our bodies with thoughtful choices lays a vital foundation for emotional resilience and cognitive well-being.Embracing this connection invites us to view meals not just as fuel, but as deliberate acts of self-care—quiet moments where science and soul meet. In understanding this delicate balance, we empower ourselves to nurture both body and mind, one bite at a time.