In the quiet hum of hospital wards and the swift pace of emergency rooms, a new kind of caregiver has emerged—not made of flesh and blood, but of algorithms and data. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming modern healthcare,weaving its way into diagnostics,treatment plans,and patient management with unprecedented precision and speed. As the line between technology and medicine blurs,this silent partner promises to redefine how we understand health and healing,raising profound questions about the future of care itself. This article explores the multifaceted role of AI in today’s healthcare landscape, examining its potential, challenges, and the delicate balance between human intuition and machine intelligence.
The Transformative Impact of AI on Diagnostic Accuracy
The fusion of artificial intelligence and medical diagnostics has ushered in a new era where precision meets speed. Advanced algorithms can now analyze vast datasets—from medical imaging to genetic facts—with unprecedented accuracy.This allows clinicians to detect diseases at their earliest stages, frequently enough before symptoms even arise. The result is a meaningful reduction in misdiagnoses and delayed treatments, which traditionally have posed major challenges in healthcare.
Key advantages AI brings to diagnostics include:
- Enhanced pattern recognition beyond human capability
- Real-time data processing to support immediate clinical decisions
- Continuous learning systems that evolve with new medical knowledge
Consider the impact on radiology, where AI-powered tools can identify subtle anomalies in imaging scans, often missed by the naked eye. A study published by the National Institutes of Health highlights how these technologies improve detection rates of critical conditions such as early-stage cancer. Moreover, integration with electronic health records allows personalized diagnostics tailored to each patient’s unique profile.
| Diagnostic Challenge | Traditional Accuracy | AI-Enhanced Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer Detection | 85% | 95%+ |
| Diabetic Retinopathy Screening | 80% | 90%+ |
| Skin Lesion Classification | 78% | 93%+ |
As AI continues to evolve,its role in diagnostic medicine will deepen,making healthcare not onyl more effective but also more accessible worldwide. Institutions like the World health Organization emphasize the importance of adopting AI responsibly to enhance global health outcomes.
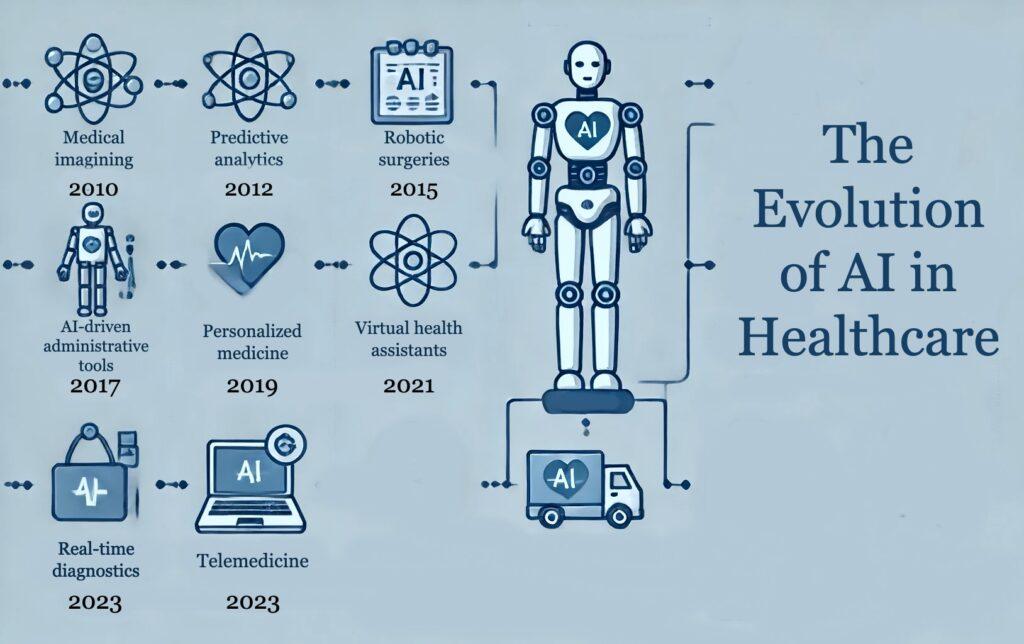
Leveraging Machine Learning for Personalized Treatment Plans
In today’s healthcare landscape, harnessing advanced algorithms enables clinicians to create treatment protocols tailored specifically to an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history. Machine learning models analyze vast datasets—ranging from electronic health records to real-time monitoring devices—to identify subtle patterns invisible to the human eye. This precision not only improves therapeutic outcomes but also minimizes adverse effects by ensuring interventions are as unique as the patients themselves.
Key benefits of this approach include:
- Dynamic adaptation: Treatment recommendations evolve continuously with new data inputs, allowing care plans to stay relevant over time.
- Predictive insights: Algorithms can anticipate disease progression or complications, supporting proactive management strategies.
- Resource optimization: Personalized plans reduce unnecessary testing and hospital visits, enhancing efficiency across healthcare systems.
Consider the following simplified comparison of traditional vs. machine learning-driven treatment planning:
| aspect | Traditional Approach | ML-Driven Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Data utilization | Limited to clinical guidelines and physician experience | Incorporates multi-dimensional patient data and real-time updates |
| Customization | General standardized protocols | Highly individualized treatment plans |
| Outcome Prediction | Based on population averages | Personalized risk and response forecasts |
For deeper insights into machine learning applications in medicine, the Nature Machine Intelligence collection offers a extensive repository of peer-reviewed research and breakthroughs.
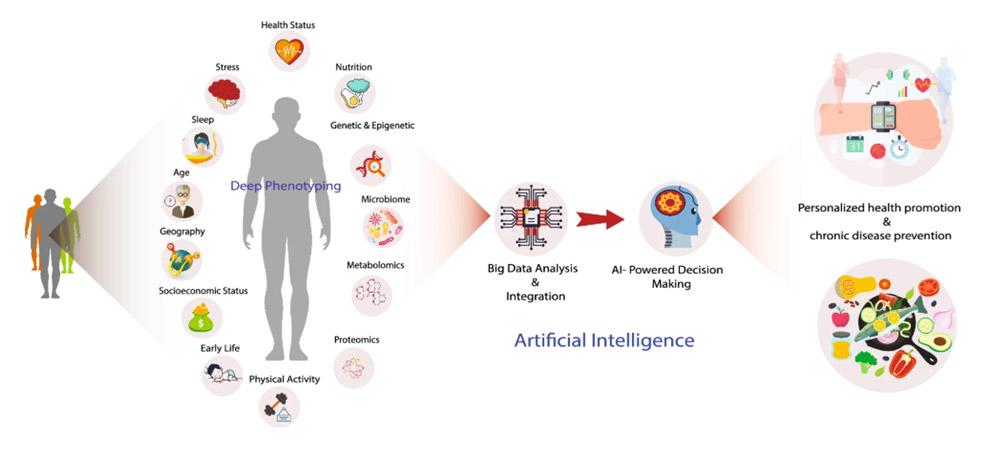
AI-Driven Data analytics Enhancing Patient Outcomes
Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence in data analytics has revolutionized how healthcare providers deliver care. By sifting through vast datasets—from electronic health records to real-time patient monitoring—AI algorithms identify subtle patterns that might elude even the most experienced clinicians. This capability allows for early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and proactive interventions that significantly improve patient outcomes.
Several key applications illustrate the transformative effect of AI-driven analytics:
- Predictive modeling to forecast disease progression and complications, enabling timely care adjustments.
- Risk stratification that helps prioritize patients requiring immediate attention.
- Optimized resource allocation ensuring critical medical equipment and staff are efficiently deployed based on predicted demand.
| AI Application | Impact on Patient Care |
|---|---|
| Real-time Diagnostics | Reduced diagnosis time by 30% |
| Treatment Personalization | Increased efficacy by 25% |
| Hospital Readmission Prediction | Lowered readmission rates by 15% |
For those interested in the broader landscape of AI’s impact on healthcare, comprehensive insights are available at NIH and WHO. These organizations explore ongoing research and emerging technologies shaping the future of medicine.
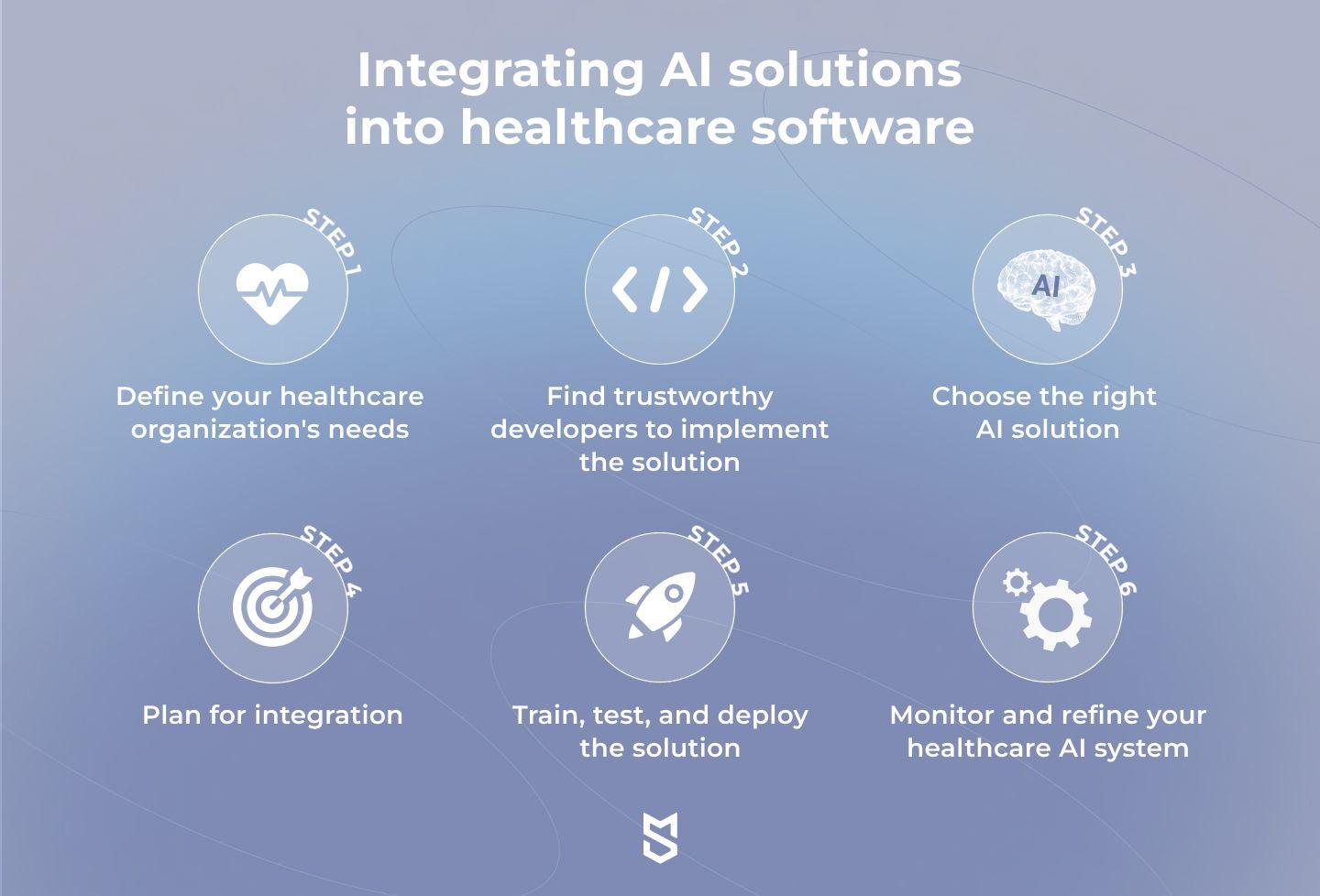
Ethical Considerations and Challenges in Healthcare AI Integration
Integrating artificial intelligence into healthcare presents a complex landscape where innovation must balance with responsibility. The potential for AI to enhance diagnostics,personalize treatment plans,and streamline administrative tasks is immense,yet it frequently enough confronts significant ethical dilemmas.Key among these is patient privacy, as AI systems require vast amounts of sensitive data — making robust security and consent protocols non-negotiable.Without transparency in how algorithms process information, the risk of unconscious bias can lead to unequal care outcomes across different demographics.
Moreover, accountability remains a critical challenge. When AI-driven recommendations directly impact patient health, questions arise: who bears responsibility if errors occur—the developers, healthcare providers, or institutions? Establishing clear frameworks that define AI’s role and limitations is essential to preserve trust. To navigate these complexities, healthcare professionals and technologists should collaborate closely, guided by principles emphasizing:
- Fairness: Eliminating bias and ensuring equitable access to AI benefits.
- Transparency: Making AI decision-making processes understandable and auditable.
- Data Integrity: Protecting patient information with strict confidentiality measures.
- Human Oversight: Keeping healthcare practitioners actively involved in AI-assisted decisions.
| Ethical Challenge | Potential impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| bias in Algorithms | Disparities in treatment accuracy | Diverse data training & regular audits |
| data Privacy | Unauthorized access or leaks | Encryption & strict access controls |
| Accountability | Unclear liability in malpractice | Regulatory frameworks & clear guidelines |
To further understand these ethical issues and frameworks shaping AI’s future in medicine, consult guidance from leading organizations such as the World Health Organization and ethical principles outlined by the Nuffield Council on bioethics. By approaching AI integration with thoughtful scrutiny, healthcare systems can harness its transformative power responsibly and inclusively.

Strategies for Seamless Adoption of AI Technologies in Medical Practice
Integrating artificial intelligence into medical environments requires more than just advanced technology; it demands a thoughtful transformation of workflows and mindsets. A key component is educating healthcare professionals on AI’s capabilities and limitations, ensuring they view AI as an empowering partner rather than a competitor. Hands-on training workshops and continuous learning programs can foster confidence and help clinicians harness AI tools effectively.
equally important is the establishment of interdisciplinary teams where data scientists, IT specialists, and medical practitioners collaborate closely. This synergy ensures AI algorithms are tailored to real-world clinical challenges, improving both accuracy and usability. Additionally, obvious communication with patients about AI’s role underpins trust and ethical acceptance, especially in sensitive contexts like diagnostics or treatment planning.
- Robust data governance: Protecting patient privacy while ensuring data quality for AI training.
- Incremental implementation: Starting with pilot projects to measure impact and refine systems.
- Feedback loops: Continuous monitoring and updating of AI models based on clinician input and outcomes.
| Strategy | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Educational Workshops | Improves adoption rates | Hands-on AI simulation training |
| Interdisciplinary Teams | Enhances solution relevance | Collaboration between radiologists and data engineers |
| Incremental Rollout | Manages risk and gathers feedback | Pilot AI-assisted diagnostics |
For further detailed frameworks and best practices, authoritative resources such as the World Health Organization’s guide on digital health and NIH’s review on AI adoption in healthcare provide invaluable insights into creating responsible AI ecosystems.
Closing Remarks
As the pulse of innovation quickens, AI continues to weave itself into the fabric of modern healthcare—reshaping diagnoses, personalizing treatments, and anticipating needs with a precision once thought impossible. While challenges remain, the collaborative dance between human insight and artificial intelligence promises a future where healthcare is not only smarter but more compassionate. Embracing this evolving partnership, we stand on the threshold of a new era, where the art and science of healing move forward together, guided by the possibilities that AI unfolds.



