As the hum of combustion engines gradually fades into memory, a new era of transportation quietly accelerates on the horizon. Electric vehicles (EVs), once a niche curiosity, are now steering the world toward a cleaner, smarter future. Yet, the promise of this revolution hinges not only on the cars themselves but equally on the invisible web of charging stations that power them. This article explores the evolving landscape of electric vehicles and their charging infrastructure, delving into the technologies, challenges, and innovations that will shape how we move in the decades ahead.
The Evolution of Electric Vehicle Technology and Its Impact on Transportation
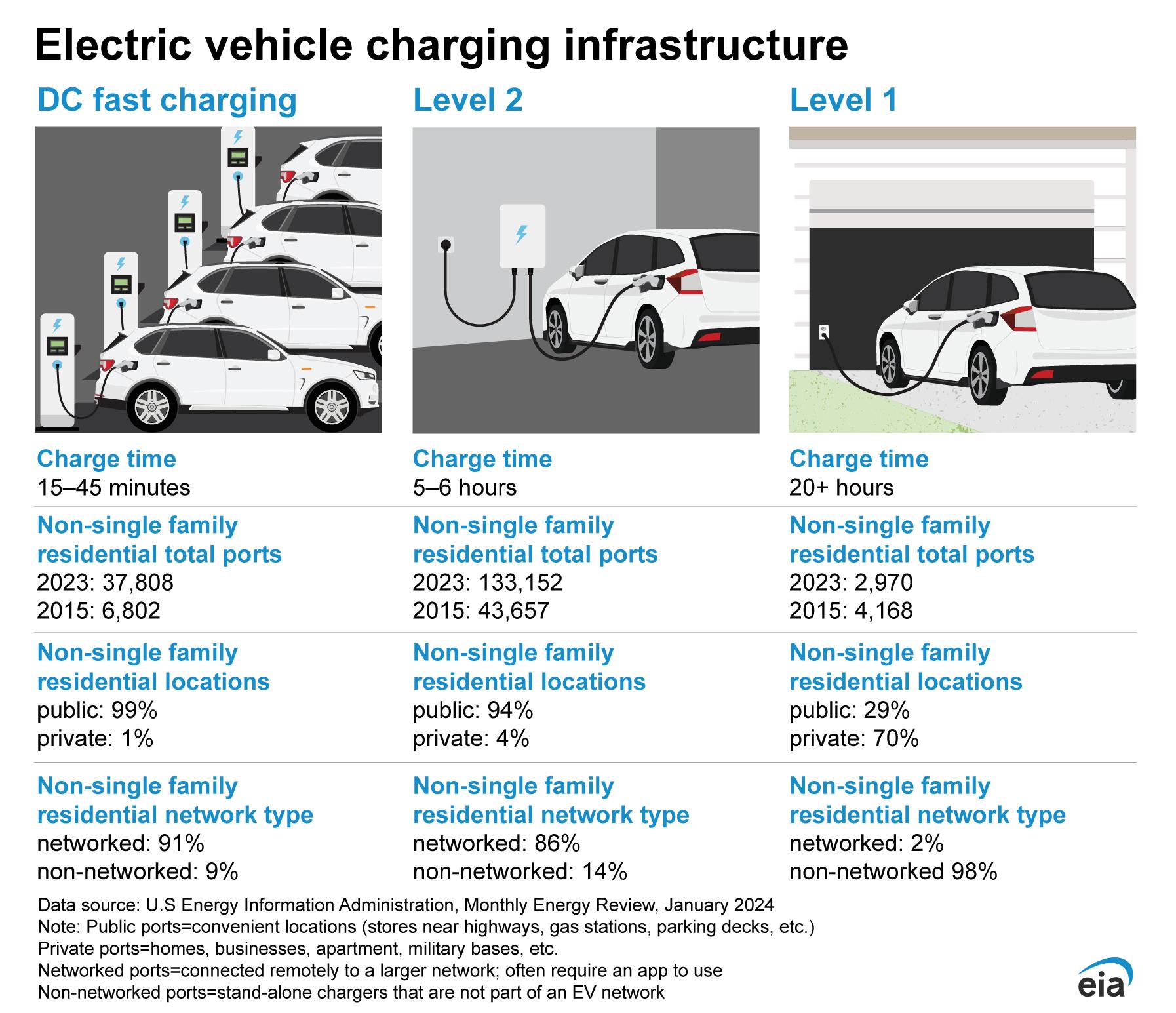
The shift from traditional combustion engines to electric drivetrains has revolutionized how we think about mobility. Early electric vehicles (evs) were limited by short ranges and slow charging times, but advancements in battery chemistry, power electronics, and energy management have dramatically improved performance. Today’s EVs boast longer ranges,faster acceleration,and more efficient energy use,setting new standards for sustainability and innovation in transportation.
Charging infrastructure has evolved alongside vehicle technology, transforming from sparse, inconvenient options into a rapidly expanding network that supports fast and ultra-fast charging. Smart charging stations integrated with renewable energy sources and grid management systems are not only reducing carbon footprints but also enhancing user convenience. This synergy between vehicles and infrastructure is vital for widespread EV adoption and paves the way toward a cleaner, interconnected transport future.
Key Milestones in EV Technology
- Lithium-ion Batteries: Enabling higher energy density and longer lifespans.
- Fast Charging Protocols: Reducing charging time from hours to minutes.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Systems: Allowing EVs to feedback energy to the grid.
- autonomous Driving Integration: Combining EV efficiency with cutting-edge AI.
| Year | Battery Range (miles) | Charging time (minutes) | Notable Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 100 | 120 | Introduction of lithium-ion |
| 2015 | 200 | 60 | Rapid charging stations |
| 2020 | 300 | 30 | V2G pilot programs |
| 2024 | 400+ | 15 | Solid-state battery breakthroughs |
For a deeper dive into the transition from fossil fuels to electrification,you can explore resources from U.S. Department of Energy – Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable energy and learn about smart grid developments at International Energy Agency.

Innovations in Charging Infrastructure Transforming User Experience
The landscape of electric vehicle charging is undergoing a revolutionary shift, driven by advancements that prioritize speed, convenience, and smart technology integration. Today’s charging stations are no longer just functional utilities; they are evolving into refined hubs capable of delivering seamless user experiences tailored to individual needs.Innovations such as ultra-fast charging, wireless charging pads, and AI-powered station management are making electric vehicle (EV) ownership more accessible and attractive than ever before.
Key features transforming charging experiences include:
- Ultra-fast chargers reducing the average charging time to under 15 minutes, rivaling traditional refueling stops.
- Dynamic load balancing systems that optimize energy distribution, preventing grid overloads and lowering costs.
- Integrated mobile apps providing real-time charger availability, remote monitoring, and reservation capabilities.
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology enabling EVs to feed energy back to the grid during peak demand, creating a more sustainable ecosystem.
| Innovation | Impact | Estimated Adoption timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Wireless Charging Pads | Eliminates plugs, boosts convenience | 2025-2027 |
| AI-Managed Stations | Optimizes charger use, reduces wait times | 2024-2026 |
| Ultra-Fast Superchargers | Makes charging as fast as refueling | 2023-2025 |
For further insights into these cutting-edge developments, resources such as the U.S. Department of Energy and International Energy Agency offer comprehensive reports and forecasts.Additionally, technology firms like Tesla’s Supercharger Network demonstrate practical applications of these transformative charging innovations.
Addressing Energy demand and Sustainability in EV expansion
as the electric vehicle (EV) market accelerates, meeting the surging energy demand while ensuring sustainability becomes paramount.The integration of renewable energy sources,such as wind and solar,with EV charging infrastructure offers a promising solution. By leveraging smart grids and energy storage systems, we can balance peak loads and reduce strain on the power network, ensuring a reliable and eco-pleasant charging experience.
Innovative approaches like vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology enable EVs to act as mobile energy reserves, supplying power back to the grid during high-demand periods. This symbiotic relationship not only stabilizes energy flow but also creates new avenues for utility companies and consumers alike. Critical factors to focus on include:
- Scalable infrastructure: Deploying fast-charging stations powered by clean energy.
- Grid modernization: Incorporating AI-driven demand forecasting for efficient resource allocation.
- Policy incentives: Encouraging businesses and homeowners to install solar panels coupled with EV chargers.
| Energy Source | CO₂ Emissions (g/km) | charge Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Solar | 0 | excellent |
| Wind | 0 | Excellent |
| Grid Average | 120 | Moderate |
| Fossil Fuels | 240 | Poor |
For further insights on sustainable energy integration, institutions like
Strategic Policy Frameworks to Support Widespread EV Adoption
To catalyze a mass transition to electric vehicles, governments and industry leaders must implement comprehensive policy frameworks that go beyond subsidies and tax incentives. These frameworks should facilitate infrastructure development, streamline regulatory procedures, and foster public-private partnerships. Robust zoning laws, standardized charging protocols, and dynamic electricity pricing models form the backbone of an environment that encourages both manufacturers and consumers to embrace EV technology.
Key strategic measures include:
- Mandates for new building codes to require EV-ready wiring and charging stations in residential and commercial developments, reducing future retrofitting costs.
- Investment in grid modernization to support increased electricity demand and enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration,enhancing sustainability and resilience.
- Support for rural and underserved areas to ensure equitable access to EV infrastructure, closing the gap between urban and remote communities.
| Policy Element | Primary Objective | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Infrastructure Mandates | Scaffold nationwide accessibility | Reduced range anxiety, increased user confidence |
| Incentives for grid Upgrades | Ensure reliable energy supply | Enhanced grid stability and integration |
| Equity-Based Funding Programs | Promote inclusivity and access | Broader demographic EV adoption |
For more data on effective EV policies and their global impact, explore resources from the International Energy Agency, the U.S. Department of Transportation, and insights from the Environmental Protection Agency.

Building a Collaborative Ecosystem for Future Mobility Solutions
Creating a seamless network for electric mobility hinges on shared innovation and partnerships among automakers, governments, and technology providers. by fostering a collaborative ecosystem, the industry can accelerate breakthroughs that address infrastructure gaps and user experience challenges. Open data platforms and standardized protocols enable various stakeholders to work in unison,minimizing fragmentation and promoting interoperability across charging networks.
Key elements driving this cooperation include:
- Joint ventures to build scalable and accessible charging infrastructures
- Integration of renewable energy to power stations sustainably
- Shared R&D initiatives focusing on cutting-edge battery technologies and smart grid connectivity
Consider the following comparison of collaborative ecosystem benefits versus traditional siloed approaches:
| Aspect | collaborative Ecosystem | Siloed Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Innovation Speed | Accelerated through shared expertise | Slower, limited to internal teams |
| Infrastructure Coverage | Broad and interconnected | Fragmented and inconsistent |
| user Experience | unified, reliable, and easy access | Varies widely by provider |
For further insights on industry collaboration models, visit the International Energy Agency’s Global EV Outlook or explore the UK Department for Transport’s electric vehicle infrastructure strategies.
In Summary
As we stand on the brink of a transportation revolution, the future of electric vehicles and charging stations promises a landscape rich with innovation, sustainability, and possibility. Roads once dominated by gasoline engines are gradually transforming into arteries of clean energy, supported by a growing network of smart, accessible charging hubs. While challenges remain—from infrastructure development to technological refinement—the momentum is undeniable. The journey toward electrified mobility invites us all to rethink how we move, power our lives, and connect with the world around us.In embracing this future, we’re not just driving cars; we’re steering toward a more sustainable horizon for generations to come.





