In teh intricate symphony of our body’s functions,inflammation often plays a discordant note—sometimes a necessary response to injury,but other times a silent saboteur of health. While inflammation is a natural mechanism meant to protect and heal, chronic inflammation has been linked to a host of modern ailments, from heart disease to arthritis. Fortunately, the foods we choose to nourish ourselves with can either fan the flames or help soothe the underlying fire.This article embarks on a journey thru the vibrant world of nutrition, exploring how mindful dietary choices can serve as powerful tools to reduce inflammation and promote lasting wellness.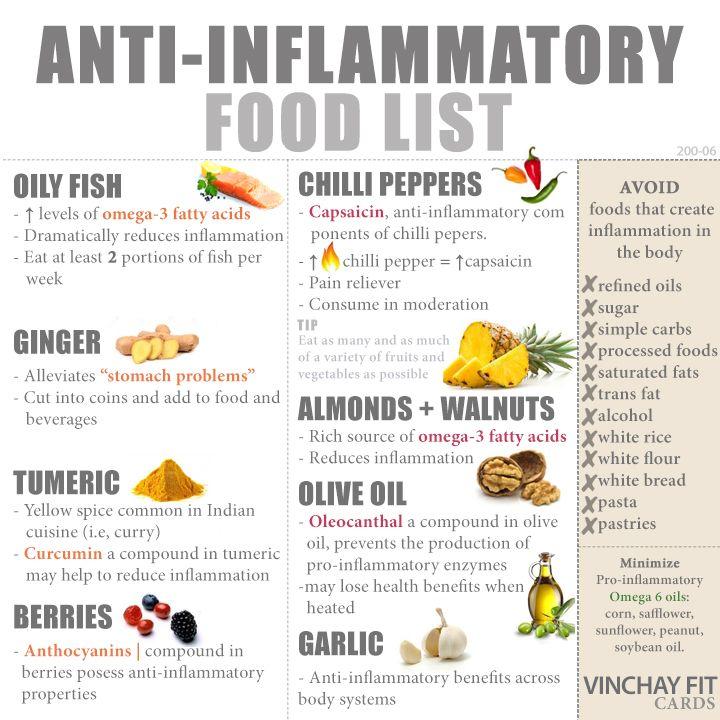
Understanding Inflammation and Its Dietary Triggers
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, acting as a defense mechanism to protect and repair tissues.However,when inflammation becomes chronic,it can contribute to several health issues,including heart disease,arthritis,and even certain cancers. One of the most manageable factors influencing inflammation is diet. Certain foods have been identified as dietary triggers that may exacerbate inflammation, including processed sugars, trans fats, and excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates. Understanding which foods fuel inflammation helps in crafting a meal plan that supports overall health and reduces the burden on the immune system.
To create an anti-inflammatory diet, focus on incorporating nutrient-rich ingredients known for their healing properties. Foods such as leafy greens,fatty fish rich in omega-3s,and colorful fruits offer antioxidants and essential fatty acids that combat oxidative stress. Avoid common triggers listed below to better control inflammatory responses:
- Excessive red meat consumption
- Refined sugars and high-fructose corn syrup
- Processed snacks and baked goods with trans fats
- Excessive alcohol intake
| Inflammatory food | Impact on Body | Suggested Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Processed Meats | Increases inflammatory markers | Lean poultry or plant-based proteins |
| Sugar-sweetened Beverages | Raises blood sugar levels rapidly | Herbal teas or infused water |
| Refined Carbohydrates | Spikes insulin and inflammation | Whole grains like quinoa or oats |
For further guidance on adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, resources like the Healthline nutrition section offer comprehensive insights backed by scientific research. Recognizing how your meals interact with your body’s inflammatory processes is a powerful step towards long-term wellness.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Incorporate Into Your Daily Meals
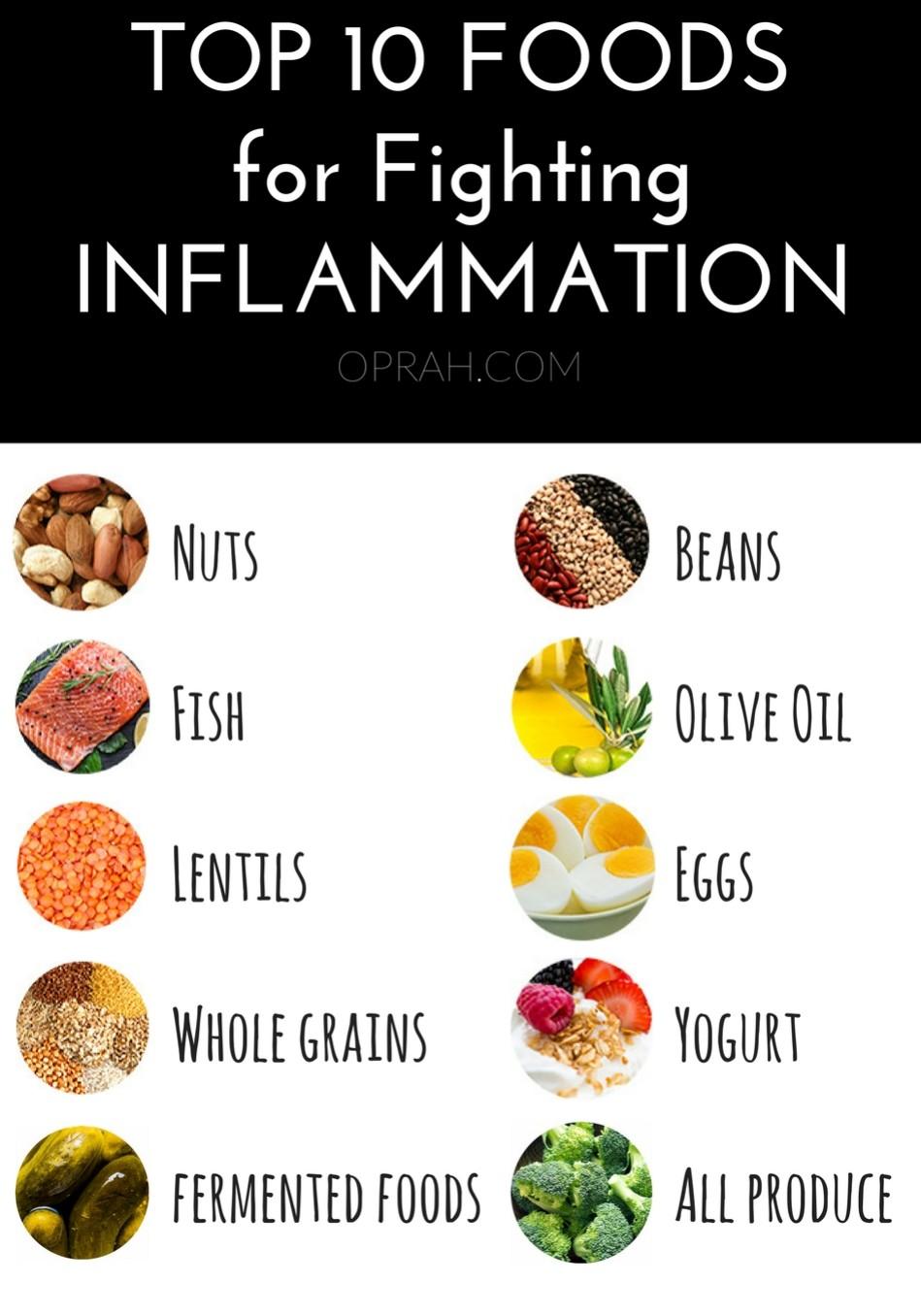
embracing a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can significantly ease chronic inflammation and support overall health. Key players include vibrant fruits like blueberries and cherries, celebrated for their antioxidants, and leafy greens such as spinach and kale, packed with vitamins and minerals. Adding fatty fish,such as salmon and mackerel,brings omega-3 fatty acids,which are well-known for their inflammation-reducing properties. Don’t overlook nuts like walnuts and almonds, as they provide essential healthy fats and fiber. Incorporating these ingredients daily helps nurture your body’s defenses and improve long-term wellness.
To better understand the benefits of these foods, consider this speedy guide:
| Food group | Key Nutrient | Inflammation Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits (Berries) | Antioxidants | Protect cells from oxidative stress |
| Leafy Greens | Vitamins A, C, K | Support immune regulation |
| Fatty Fish | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduce pro-inflammatory markers |
| Nuts | Healthy Fats | Lower inflammation levels |
For scientific insights on the power of these foods, explore resources like NCBI’s studies on anti-inflammatory diets or visit the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health to discover practical recommendations supported by research.

The Role of Balanced Nutrients in managing Chronic Inflammation
chronic inflammation is frequently enough the silent culprit behind many health issues, but a thoughtfully balanced diet can play a decisive role in turning the tide. Incorporating an array of essential nutrients not only helps to calm inflammatory pathways but also supports the body’s natural healing processes. Omega-3 fatty acids,found in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds,are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that help reduce cytokine production and joint inflammation. Simultaneously occurring,antioxidants such as vitamins C and E combat oxidative stress,a key driver of chronic inflammation,by neutralizing harmful free radicals.
For optimal results, focus on a diet rich in:
- Colorful vegetables and fruits – packed with polyphenols and flavonoids that protect cells
- Whole grains – high in fiber, which supports gut health and reduces inflammatory markers
- Lean protein sources – such as poultry and legumes to maintain muscle mass without excess saturated fat
- Healthy fats – including olive oil and nuts that foster anti-inflammatory responses
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Anti-Inflammatory Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Salmon, Walnuts, Flaxseeds | Reduces cytokine production |
| Vitamin C | Oranges, bell Peppers, Strawberries | Neutralizes free radicals |
| Fiber | Oats, Barley, Lentils | Supports gut microbiota |
| Polyphenols | Berries, green Tea, Dark Chocolate | Protects against cellular damage |
Balancing these key nutrients helps create an internal environment where inflammation is less likely to escalate into chronic disease. For more detailed insights on nutrition’s impact on inflammation, visit national Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.

Practical Meal planning Tips for Sustained Inflammation Reduction
Maintaining a balanced diet that consistently incorporates anti-inflammatory foods is key to managing chronic inflammation effectively. Plan your meals around ingredients rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber—such as fatty fish, leafy greens, nuts, and berries. Preparing meals in advance can help you avoid last-minute unhealthy choices. Consider using slow cookers or batch cooking methods to create nutrient-dense dishes that retain their anti-inflammatory benefits throughout the week. Integrating herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, and garlic not only adds flavor but also introduces potent anti-inflammatory compounds.
To make your meal planning even more effective, use a simple chart to balance your macronutrients and anti-inflammatory ingredients daily. Below is a quick reference table that can guide your shopping and cooking habits for sustained inflammation control:
| Food Category | Anti-Inflammatory Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fats | Olive oil, walnuts, flaxseeds | Reduce oxidative stress, improve heart health |
| Proteins | Salmon, lentils, chickpeas | Support tissue repair, reduce inflammation markers |
| Vegetables & Fruits | Spinach, blueberries, broccoli | High antioxidants, promote gut health |
| Spices & Herbs | Turmeric, ginger, rosemary | Inhibit inflammatory molecules |
For more insights on anti-inflammatory diets, check out the resources provided by the National center for Complementary and Integrative Health and the detailed guidelines on Healthline.
Final Thoughts
In the intricate dance of our body’s wellness, reducing inflammation through diet is a step toward harmony and balance. By choosing nourishing foods rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and vibrant nutrients, we give our bodies the tools to soothe irritation and promote healing from within. While no single meal is a magic fix, embracing these dietary choices consistently can help rewrite the story of inflammation—one plate at a time. The journey toward a calmer, healthier you begins with what’s on your fork.