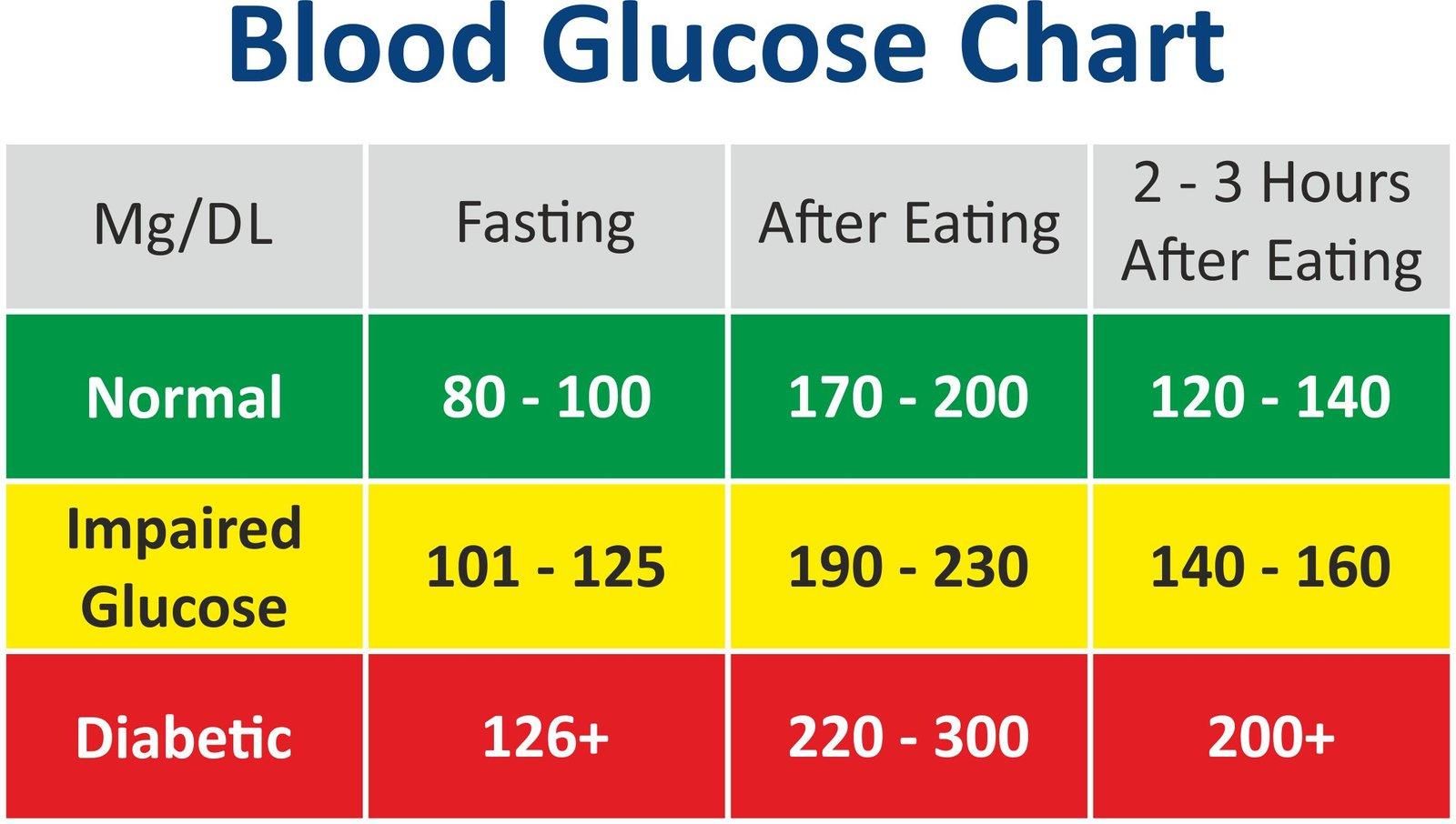
In the intricate dance of our body’s functions, blood sugar levels play a starring role, quietly influencing energy, mood, and overall well-being. Maintaining these levels within a healthy range is not just a matter of chance but a nuanced balance shaped by daily choices and habits. Whether you’re seeking to prevent spikes and crashes or aiming to manage existing concerns, understanding how to keep blood sugar steady is a vital step toward vibrant health. This article delves into practical strategies and insights to help you navigate the path to balanced blood sugar—empowering you to feel your best, one steady step at a time.
Understanding the role of Nutrition in Blood Sugar Regulation
Blood sugar regulation is deeply influenced by the foods we consume and the timing of our meals. When carbohydrates are ingested, they break down into glucose, causing a rise in blood sugar levels. however, not all carbs affect blood sugar equally. Complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, are digested more slowly, providing a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream. Incorporating these foods into your diet, along with a balance of protein and healthy fats, helps maintain stable blood sugar. Additionally, the role of fiber intake is critical, as it slows glucose absorption and promotes digestive health.
Understanding how different nutrients impact blood sugar can empower more informed dietary choices. Here’s a concise overview of key nutrients and their effects:
| Nutrient | Impact on Blood Sugar | Optimal Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | Slows glucose absorption, reduces spikes | Vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains |
| Protein | Promotes satiety, stabilizes blood sugar | Lean meats, tofu, beans, eggs |
| Healthy Fats | Delays digestion, supports insulin sensitivity | Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil |
| Refined Carbs & Sugars | Rapid glucose spikes, insulin resistance risk | Limit consumption of sweets, white bread, sugary drinks |
- Strategic meal timing: Eating smaller, balanced meals throughout the day can prevent extreme blood sugar fluctuations.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake supports kidney function, helping to filter excess sugar.
- regular physical activity: Exercise improves glucose uptake by muscles and enhances insulin sensitivity.
For a extensive guide on nutrition and blood sugar management, consider reputable sources like the American Diabetes Association and the CDC Nutrition Guidelines.

Incorporating Physical Activity for Stable Glucose Levels
Engaging in regular physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining balanced blood sugar levels. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity,allowing your muscles to absorb glucose more efficiently and reduce circulating sugar in the bloodstream.Even moderate activities, like brisk walking or cycling, performed consistently can lead to meaningful improvements in glucose metabolism. Incorporating a variety of movements, including both aerobic and strength training, creates a synergistic effect that stabilizes glucose and supports long-term metabolic health.
To make the most of physical activity for glucose control, consider these key strategies:
- consistency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly, as recommended by CDC.
- Variety: Combine aerobic exercises like swimming or jogging with resistance training to boost insulin sensitivity across muscle groups.
- Timing: Light post-meal activities, such as walking, can blunt blood sugar spikes more effectively.
- Monitoring: Track your glucose responses and adjust routines in collaboration with healthcare professionals.
| Exercise Type | Effect on Glucose | Recommended Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic | Improves insulin sensitivity | 30–60 mins/session |
| Strength Training | Increases muscle mass for glucose disposal | 2–3 times/week |
| Versatility & balance | Supports overall physical wellbeing | Daily stretches |
For more detailed guidance, the American Diabetes Association offers comprehensive resources aimed at integrating exercise safely into your lifestyle.
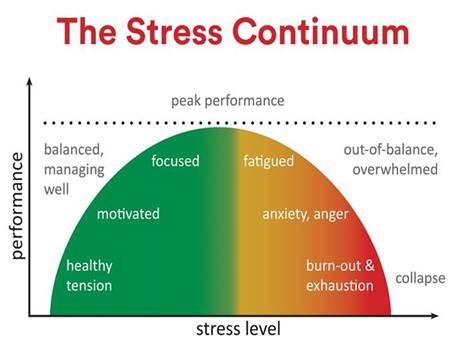
Effective Stress Management Techniques to Prevent Spikes
Managing your stress levels plays a crucial role in stabilizing blood sugar, as emotional stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause unwanted glucose spikes. Incorporating practices such as mindful breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and regular physical activity can definitely help regulate these hormonal responses effectively. Creating a daily routine with dedicated moments for stress relief can transform the way your body handles glucose during challenging situations, keeping levels balanced throughout the day.
Key techniques to incorporate daily:
- Engage in at least 30 minutes of aerobic exercise
- Practice mindfulness meditation or yoga
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule for proper recovery
- limit exposure to digital screens before bedtime to improve rest quality
- Seek social support or professional counseling when needed
| Technique | Benefit | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Mindful Breathing | Reduces cortisol levels | Daily,5-10 min |
| Aerobic Exercise | Improves insulin sensitivity | 3-5 times/week |
| Yoga | Balances nervous system | 2-3 times/week |
For those interested in deepening their understanding of stress and metabolic health,resources such as the CDC’s guide on stress management for diabetes and details from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) offer evidence-based advice that can enhance your self-care strategy. These scientifically grounded techniques empower you to keep your blood sugar within a healthy range without compromising your well-being.
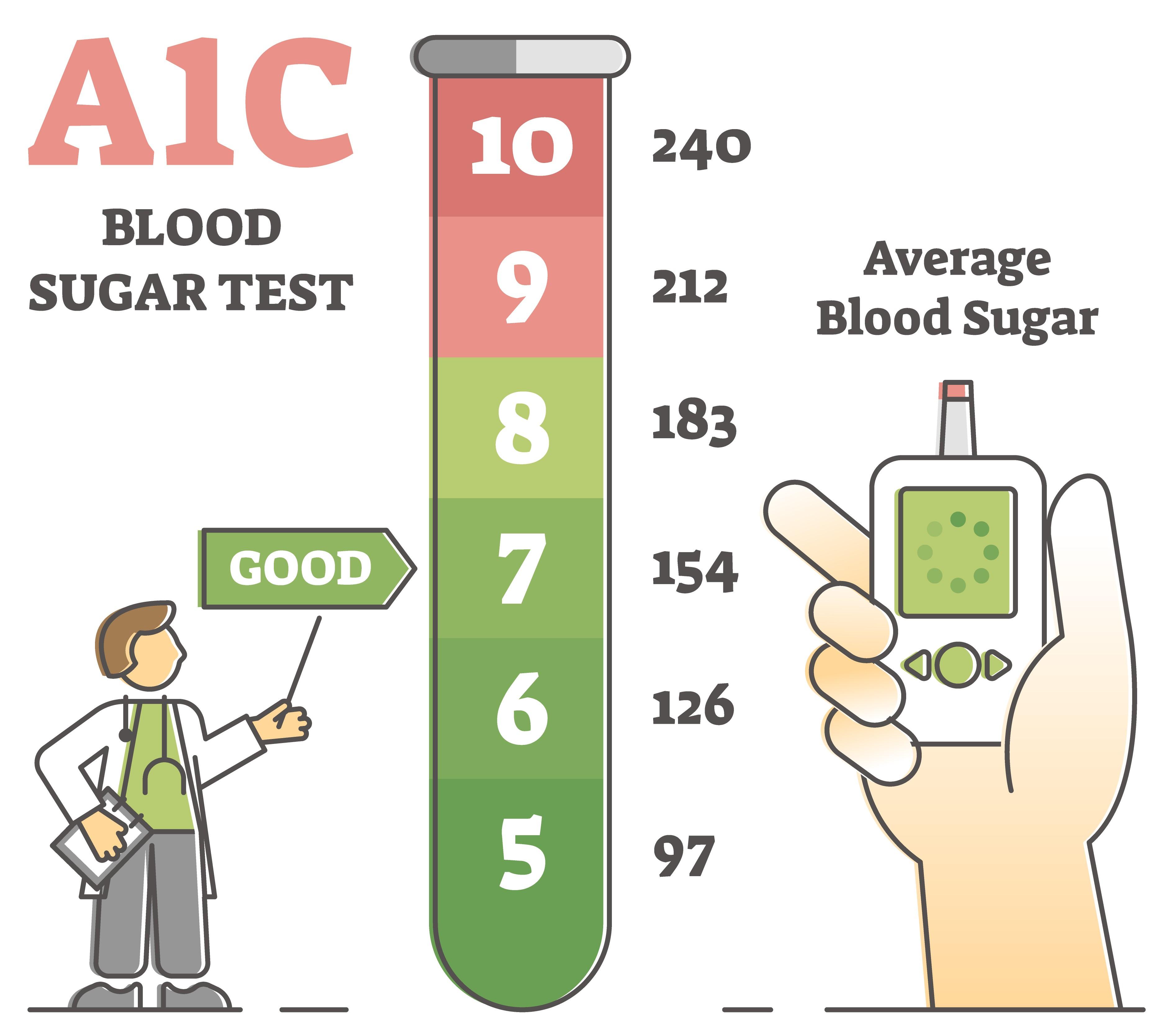
Monitoring and Adjusting Lifestyle Habits for Long-term Control
Consistent self-monitoring is a cornerstone for maintaining balanced blood sugar levels. Utilize tools like continuous glucose monitors or conventional glucometers to track your readings throughout the day, especially before and after meals. This practice helps you understand how different foods, physical activities, and stress levels influence your glucose.Keep a detailed journal noting your daily habits alongside your blood sugar results — over time, patterns will emerge, empowering you to make informed decisions. Websites like CDC Diabetes Resources offer excellent guides on blood glucose monitoring techniques and standards.
Adapting your lifestyle requires flexibility and awareness. Be prepared to adjust your meal plans, physical activity routines, or sleep schedule based on your glucose monitoring outcomes. Here are some practical adjustments to consider:
- Nutrition: Emphasize low glycemic index foods, fiber-rich vegetables, and balanced macros.
- Exercise: Incorporate consistent aerobic and resistance training, but modify intensity based on your glucose levels.
- Sleep: Aim for 7–9 hours of quality rest to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management: Practice mindfulness or gentle yoga, both shown to reduce cortisol-related glucose spikes.
| Habit | Recommended frequency | Impact on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Sugar Monitoring | Multiple times daily or as advised | Identifies spikes and trends |
| Balanced Meals | 3–5 times a day | Prevents abrupt glucose fluctuations |
| Physical activity | Most days of the week | Enhances insulin sensitivity |
| Stress Reduction | Daily practice | Lowers cortisol-induced glucose spikes |
For a deeper dive into lifestyle adjustments and how they modulate blood sugar, explore insights at American Diabetes Association - Lifestyle Management, a highly trusted source for evidence-based strategies.
In Retrospect
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is not just a goal—it’s a lifelong journey that blends mindful choices with everyday habits. By embracing a balanced diet, staying active, managing stress, and staying informed, you empower yourself to live with vitality and stability. Remember, it’s the small, consistent actions that harmonize your body’s rhythm and keep your blood sugar in check. So, take that first mindful step today, and let your well-being flourish naturally over time.