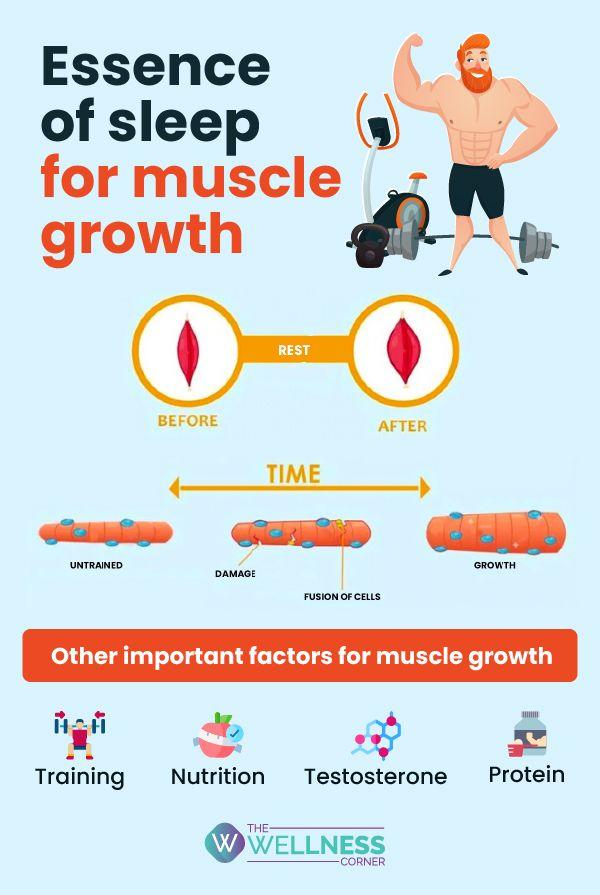
In the relentless pursuit of strength and fitness, many athletes and enthusiasts focus intently on workouts and nutrition, often overlooking a silent yet powerful ally: sleep. More than just a nightly ritual, sleep serves as a fundamental cornerstone for recovery and muscle growth. As the body retreats into rest, complex physiological processes unfold, repairing damage, restoring energy, and fostering the very foundations of strength. In this article, we will explore the critical role that sleep plays in the journey from exertion to enhancement, unveiling why those precious hours of slumber are as essential as any rep or meal in sculpting a stronger, healthier body.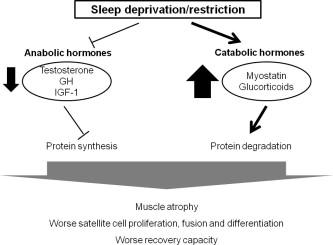
The Science Behind sleep and Muscle Repair
During deep sleep stages, notably slow-wave sleep (SWS), the body initiates critical processes that promote muscle repair and growth. This phase triggers the release of growth hormone, which plays a pivotal role in protein synthesis and tissue regeneration. Muscle fibers experience micro-tears from exercise, and it’s during these restful moments that the body efficiently repairs those fibers, making them stronger and more resilient. Additionally, sleep helps regulate cortisol, a stress hormone that, when elevated, can negatively impact muscle recovery and growth.
Several physiological mechanisms collaborate to optimize muscle recovery during sleep, such as:
- Enhanced Blood Flow: Improved circulation helps deliver essential nutrients and oxygen to muscles.
- Reduced Inflammation: Sleep modulates inflammatory responses, enabling faster healing of damaged tissues.
- Protein Synthesis Boost: Increased anabolic activity supports muscle fiber rebuilding.
| Sleep Stage | Role in Muscle Recovery | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Slow-Wave Sleep (SWS) | Growth hormone release and tissue regeneration | 1–2 hours per night |
| REM Sleep | Memory consolidation and CNS recovery | 90–120 minutes per night |
Understanding the science behind sleep’s influence on muscle repair emphasizes why quality rest is as crucial as nutrition or training. For further reading on the biochemistry of sleep and it’s muscular benefits, resources like NCBI and Sleep Foundation offer comprehensive, peer-reviewed data.
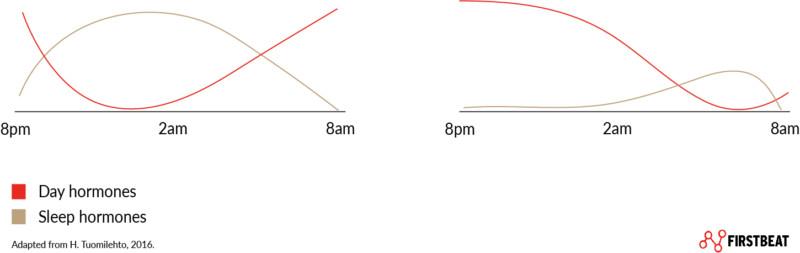
How Sleep Influences Hormone Levels for Growth
During deep sleep, the body undergoes a surge in the release of growth hormone (GH), a critical player in muscle repair and recovery. This hormone not only stimulates protein synthesis but also promotes the regeneration of muscle tissues damaged during intense workouts. Without sufficient sleep, the pulsatile release of GH is disrupted, leading to slower recovery times and diminished muscle growth potential. moreover, the balance of other key hormones such as testosterone and cortisol is closely tied to sleep quality. Optimal levels of testosterone support muscle building, while elevated cortisol—a stress hormone—can accelerate muscle breakdown and impede recovery.
- Growth Hormone: Peaks during deep sleep phases, accelerating tissue repair.
- Testosterone: Maintains muscle mass and strength, influenced by sleep duration.
- Cortisol: Excessive levels from sleep deprivation increase muscle degradation.
| Hormone | Effect on Growth | Sleep Dependency |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Hormone | Stimulates muscle repair | High during deep sleep |
| Testosterone | Supports muscle protein synthesis | Reduced with poor sleep |
| Cortisol | Breaks down muscle tissue | Elevated with sleep loss |
Understanding the intricate dance between sleep and hormone regulation can empower individuals to optimize their recovery strategies. Focus on cultivating consistent, quality sleep to harness natural hormonal cycles that fuel muscle growth and overall resilience. For scientific insights on the hormonal impact of sleep, visit NCBI and comprehensive analyses at the Sleep Foundation.

Optimizing Sleep Habits to Maximize Recovery
Quality rest is the cornerstone of efficient recovery, turning sleep into an active phase where your body rebuilds muscle tissue and balances hormones critical for growth. During deep sleep, human growth hormone (HGH) surges, which directly supports muscle repair and synthesis. To harness this natural process, consistency is key—aiming for 7-9 hours every night helps maintain strong circadian rhythms and optimizes the secretion of restorative hormones.
Creating an environment tailored for sleep maximizes recovery potential. Consider adapting your bedroom with these simple tweaks:
- Cool, dark, and quiet surroundings enhance the quality of deep sleep cycles.
- Limiting blue light exposure from screens an hour before bed supports melatonin production.
- Consistent sleep and wake times reinforce your natural body clock.
| Sleep Factor | Benefit to Recovery |
|---|---|
| Deep Sleep | HGH Surge & Muscle Repair |
| REM Sleep | Cognitive Recovery & Stress Reduction |
| Sleep Consistency | Hormonal Balance & Energy Restoration |
For evidence-based guidance, resources such as
Practical Tips for Enhancing Sleep Quality in Active Lifestyles
Optimizing your sleep environment and routine is vital for those leading active lifestyles aiming for peak recovery and muscle growth. Consider creating a dedicated sleep sanctuary by keeping your bedroom cool (around 65°F or 18°C), dark, and free from electronic distractions. This helps regulate your body’s circadian rhythm, promoting restorative deep sleep phases crucial for releasing growth hormones.Establish a consistent bedtime routine, incorporating relaxation techniques like deep breathing or reading, to signal your brain that it’s time to unwind and repair. These small adjustments can significantly improve sleep quality, translating directly to better muscle repair and performance gains.
- Limit caffeine intake: Avoid caffeine at least 6 hours before bed to prevent interference with falling asleep.
- Stay hydrated: Drink water throughout the day but reduce intake an hour before sleep to avoid nighttime disruptions.
- Incorporate light stretching: Gentle stretching before bed can relieve muscle tension and encourage relaxation.
- Manage stress: Use mindfulness apps or journaling to lower cortisol levels, which can impede recovery.
| Activity | Recommended Time Before Bed | Impact on Sleep quality |
|---|---|---|
| Exercise | 3-4 hours | Enhances deep sleep but avoid intense workouts near bedtime |
| Caffeine Consumption | 6+ hours | Prevents restlessness and delays sleep onset |
| Screen Time | 1 hour | Reduces blue light exposure, promotes melatonin production |
To dive deeper into the science of sleep and muscle growth, organizations such as Sleep Foundation and research hubs like NCBI offer extensive insights.For tailored advice on performance and recovery,Mayo Clinic presents expert-reviewed strategies balancing physical activity and rest. The key is to view sleep not as downtime but as an indispensable pillar supporting your fitness ambitions.
In Summary
As the final chapter in the story of muscle growth and recovery, sleep emerges not just as a passive rest but as an active, dynamic force shaping our physical potential. It is during these quiet hours that the body repairs, rebuilds, and prepares for the challenges ahead—transforming effort into strength, and fatigue into resilience. Embracing the essential role of sleep means unlocking a powerful ally on the path to fitness, reminding us that sometimes, the best way forward is simply to rest.In the grand symphony of muscle growth, sleep is the unsung melody that brings harmony to every note played in the gym.