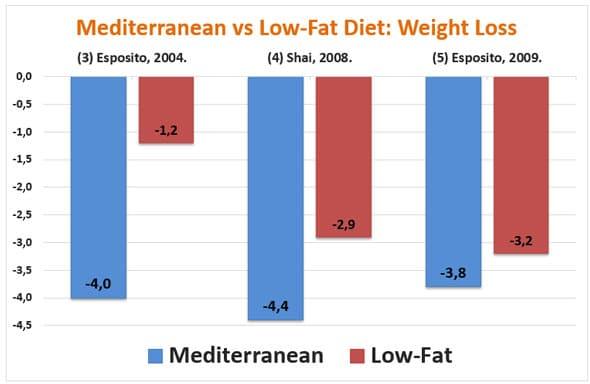
Imagine a culinary tradition where every bite not only delights the palate but also nourishes the body in profound ways. The Mediterranean diet, celebrated for its vibrant flavors and wholesome ingredients, has long been associated with a host of health benefits—from heart health to longevity. But beyond its sun-soaked allure and colorful plates lies a fascinating science that unravels how this age-old eating pattern supports well-being. In this article, we delve into the biological and nutritional mechanisms that make the Mediterranean diet more than just a meal plan—it’s a scientifically backed pathway to better health.
The Role of Healthy fats in Cardiovascular Protection
Incorporating healthy fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is central to the Mediterranean dietary approach, significantly contributing to cardiovascular health. These fats, primarily sourced from olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish, work by reducing inflammation and improving lipid profiles. For example, oleic acid, the primary monounsaturated fat in olive oil, helps lower LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol while preserving HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, ofen referred to as “good” cholesterol. Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon are renowned for their anti-arrhythmic properties and ability to decrease blood clotting, thus reducing heart attack risk.
Beyond their biochemical benefits, healthy fats also enhance nutrient absorption and contribute to satiety, aiding in better weight management—a critical factor for heart health.Some specific cardiovascular advantages include:
- Reduction of inflammation: Fatty acids help modulate inflammatory markers associated with atherosclerosis.
- Improved endothelial function: Healthy fats support the lining of blood vessels,promoting versatility and preventing stiffness.
- Blood pressure regulation: Ingredients like omega-3s can help maintain optimal blood pressure levels.
| Fat Type | Primary Source | Cardiovascular Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Monounsaturated | Olive Oil, Avocados | Lowers LDL cholesterol |
| Polyunsaturated (Omega-3) | Fatty Fish, Walnuts | Reduces inflammation & arrhythmia risk |
| Polyunsaturated (Omega-6) | Sunflower Oil, Seeds | Supports endothelial function |
For an in-depth review of the cardiovascular effects of dietary fats, consider consulting resources from the American Heart Association and detailed analyses available at NCBI. These platforms provide evidence-based insights that reinforce how integral healthy fats are to cardiovascular protection within the Mediterranean diet framework.

Antioxidants and Their Impact on Inflammation reduction
One of the cornerstone reasons the Mediterranean diet is celebrated is its abundance of antioxidants, naturally found in foods like olive oil, nuts, fruits, and vegetables.These antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals—unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and trigger chronic inflammation. By mitigating this stress, antioxidants help protect cells from damage, lowering the risk of inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, cardiovascular conditions, and even certain cancers. Notably, compounds like polyphenols and flavonoids, prevalent in Mediterranean staples, exhibit powerful anti-inflammatory properties that promote overall cellular health.
Incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into the diet leads to a synergistic effect on inflammation reduction. Key elements include:
- Extra virgin olive oil: Packed with oleocanthal, mimics effects similar to ibuprofen by reducing inflammatory enzymes.
- Colorful vegetables: Rich in vitamins C and E, these bolster the body’s defense against inflammatory destruction.
- Nuts and seeds: Sources of essential fatty acids wich modulate inflammatory pathways.
| Food | Key Antioxidants | Inflammation Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Olive Oil | Oleocanthal, Vitamin E | Reduces enzyme activity linked to inflammation |
| tomatoes | lyopene, Vitamin C | Neutralizes free radicals, protects cell walls |
| Walnuts | Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Polyphenols | Modulates inflammatory signaling pathways |
For readers interested in delving deeper into the health benefits, authoritative resources from the National Institutes of Health and World Health Institution provide complete scientific insights.
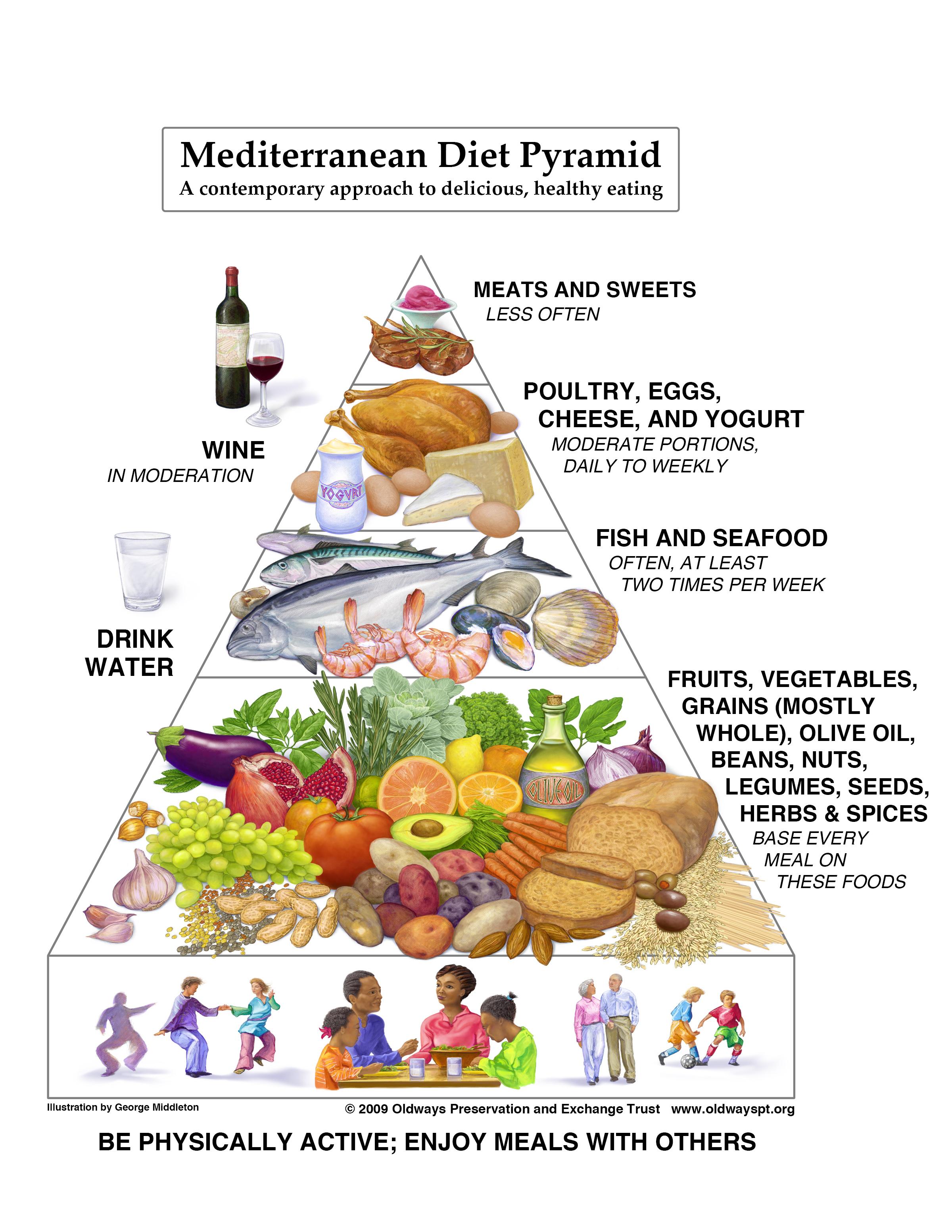
the Importance of whole Foods and Plant-Based Ingredients
Emphasizing whole foods and plant-based ingredients forms the cornerstone of the Mediterranean approach, championing natural nutrition over processed alternatives. These foods are rich in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, all of which contribute to reducing inflammation and oxidative stress—key factors in chronic disease prevention. Incorporating a diverse array of vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, and whole grains provides a symphony of nutrients that work synergistically to support cardiovascular health, improve gut microbiota, and enhance metabolic function.
Moreover, the plant-forward focus aligns with sustainable eating practices, which benefit both individual health and the planet. This dietary pattern encourages:
- Reduced intake of saturated fats, favoring healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in olives, nuts, and seeds.
- Lower glycemic index from minimally processed carbohydrate sources that stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Higher antioxidant density that helps combat free radical damage and supports longevity.
| Whole Plant Foods | key Nutritional Benefit | Research Source |
|---|---|---|
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil | Rich in polyphenols with anti-inflammatory effects | NCBI |
| Leafy Greens | High in nitrates supporting blood pressure regulation | pubmed |
| Chickpeas & Lentils | Excellent source of plant protein and fiber | Harvard T.H. Chan |
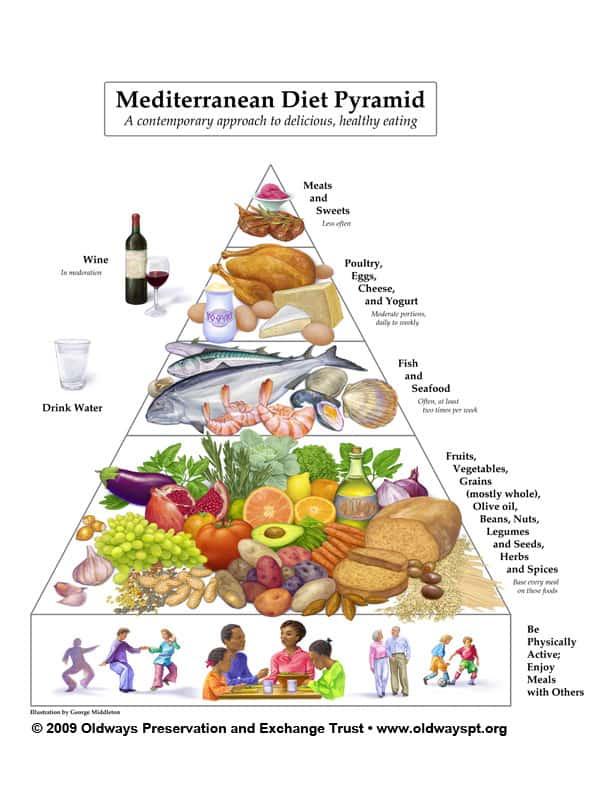
Practical tips for Incorporating Mediterranean Diet Principles Daily
Adopting Mediterranean diet principles into your daily routine doesn’t have to be complicated. Start by focusing on whole, plant-based foods like fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes, which are staples of this lifestyle. Swap out butter for heart-healthy olive oil, and make fish, especially fatty varieties like salmon or mackerel, a regular feature on your plate at least twice a week. Incorporating herbs and spices not only adds flavor but also boosts antioxidant intake, enhancing the diet’s health benefits.Remember, portion control and mindful eating are just as critically important, so savor your meals without rushing to align with the Mediterranean ethos of enjoyment and balance.
Creating a practical weekly meal plan can streamline the adoption of Mediterranean principles. Here’s a simple guide to get you started:
| Meal Time | Example Foods | Key Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Greek yogurt, fresh berries, honey, a handful of walnuts | Combine protein and healthy fats to sustain energy |
| Lunch | Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumber, tomato, feta, olive oil | Focus on colorful, nutrient-dense veggies |
| Dinner | grilled fish, steamed greens, whole grain bread | Emphasize lean proteins and fiber-rich sides |
| Snacks | Olives, a small portion of mixed nuts, fresh fruit | Choose nutrient-dense, wholesome options |
For inspiration and evidence-based guidelines on Mediterranean diet principles, visit resources such as the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health or the Centers for Disease control and Prevention (CDC). Their comprehensive insights can definitely help you tailor dietary habits that suit your lifestyle while maximizing health benefits.
Future outlook
As we peel back the layers of the Mediterranean diet, it becomes clear that its health benefits are no mere culinary coincidence.Rooted in a harmonious blend of nutrient-rich ingredients, time-tested traditions, and the science of balance, this diet offers more than a meal—it offers a pathway to wellness. Whether it’s the antioxidants in vibrant fruits, the heart-healthy fats of olive oil, or the fiber-rich whole grains, each component plays a vital role in fostering longevity and vitality. Embracing the Mediterranean way is not just about what we eat, but how we nourish our bodies and lives with mindful, flavorful choices. science doesn’t just support this diet—it celebrates it as a timeless recipe for health.